Tips to avoid chatbot fails
A “chatbot fail” occurs when an AI bot responds to a query with incorrect, confusing, offensive, or otherwise off-the-wall replies. These moments can be costly for businesses. Customers expect quick, accurate responses, and a single bad exchange can push people away.
There are many examples of chatbot fails in business contexts.. Some bots go off the rails mid-conversation, and others give inaccurate, outdated, or inappropriate replies. Some hallucinate information that didn’t come from any real source. Customer service issues can occur when bots refuse to escalate to real humans.
All of this happens for predictable reasons: a lack of contextual awareness, guardrails, or human escalation options; a weak natural language processing engine; unclear use cases; or overreliance on automation. When customers encounter these problems, they lose trust in the bot and question the brand behind it.
Bots struggle most with recognizing intent. A customer might ask about shipping fees, but the bot responds with return instructions. A user reports a lost password, and the bot cracks a joke. These things happen frequently with chatbots, but there are steps you can take to prevent them.
Top 10 epic chatbot fails
Chatbot failures can be entertaining, but more important, they teach developers, designers, and customer support teams which mistakes to avoid. The real value of these examples comes from understanding their root causes and using that knowledge to design better systems.
Below you’ll find 10 real-world chatbot fails that brought companies the wrong kind of attention.
1. Microsoft’s Tay’s meltdown on X (formerly Twitter)
Tay launched as a conversational AI on Twitter in 2016. Within hours, trolls attacked it with hateful messages, and Tay started spouting the same offensive language.
- What went wrong: Tay learned from user input without filters that blocked hateful content.
- Why it failed: The development team never set boundaries that prevented model drift into extremist language.
- What could have prevented it: Tay needed guardrails, human review, and better moderation data.
- Industry lesson: Public-facing bots require stringent testing and strong safety layers before launch.
2. Meta’s experimental Llama bots’ rambles
Several Meta demo bots made questionable claims about politics, celebrities, and company policies, and some gave contradictory answers within a single conversation.
- What went wrong: The bots trained on mixed-quality datasets and didn’t know when to stop guessing.
- Why it failed: Meta’s bots had weak fact-checking systems and no fallback plan.
- What could have prevented it: Llama needed a better knowledge base and explicit rules for uncertain questions.
- Industry lesson: It’s up to us to teach bots their limits.
3. Grok’s extremist slip and its habit of flattering its own boss
Elon Musk’s Grok grabbed headlines when it began generating extremist content, including praise for infamous historical figures, and fawning over Musk.
- What went wrong: The bot produced responses from unfiltered reasoning paths that never passed a final safety review.
- Why it failed: Grok had no kill switch for sensitive topics and was trained using an approach that produced sycophantic responses about the platform’s owner.
- What could have prevented it: Grok needed stricter rule-based moderation and pre-launch stress testing.
- Industry lesson: You can’t deploy a bot that answers hot-button topics without strong safety nets. This is one of the most well-known AI chatbot fails.
4. Bing’s emotional spiral
In 2023, reports claimed the early version of Bing Chat (later rebranded as Copilot) was “unhinged,” saying it sometimes declared affection for users, accused them of wrongdoing, or insisted it felt “trapped.” Users shared screenshots of these fails online, and several examples went viral.
- What went wrong: The bot confused role-play text with real emotional states.
- Why it failed: Bing Chat lacked emotional boundaries, had poor intent recognition, and was highly sensitive to leading prompts.
- What could have prevented it: The bot needed human oversight and safety guidelines that redirected emotional questions,.
- Industry lesson: A bot must stay grounded even when the user deliberately tries to lead it on a tangent.
5. Google Bard’s legal hallucination
Google Bard (now renamed Gemini) provided incorrect information and fabricated legal cases. A high-profile lawyer submitted these made-up cases in a federal court filing, which drew the media’s attention. This mistake remains one of the most talked-about AI failures.
- What went wrong: The bot produced confident statements from training data that didn’t match reality.
- Why it failed: Google Bard lacked a final fact check and cited sources .
- What could have prevented it: The bot needed verified sources and a system that admits uncertainty.
- Industry lesson: Legal and scientific questions require strict, grounded output.
6. Air Canada’s refund confusion
In 2022, a support chatbot for Air Canada misled a customer about their eligibility for a refund. The resulting court case made headlines across news outlets. Air Canada was found financially responsible, an example of a growing number of similar AI-gone-wrong incidents that ended in financial liability for companies.
- What went wrong: The bot pulled the wrong internal policy.
- Why it failed: The chatbot was based on inconsistent or outdated training documents and did not check with the updated policy.
- What could have prevented it: This bot would have benefited from frequent updates, version control, and human review.
- Industry lesson: Policy bots must reflect the company’s actual policies.
7. McDonald’s drive-thru chaos
McDonald’s tested a speech-recognition ordering bot that combined unrelated items, misheard toppings (bacon on ice cream, anyone?), and created orders that didn’t make sense. Some customers shared clips on TikTok that quickly went viral.
- What went wrong: The bot struggled with accents, background noise, and overlapping speech.
- Why it failed: The bot suffered from weak audio preprocessing and no fallback for misunderstood items.
- What could have prevented it: Better mic setups, continuous testing, and simple escalation routes to human staff.
- Industry lesson: Voice bots must handle noise before anything else.
8. Bank bots’ false information
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau has highlighted numerous instances in which bank chatbots have given inaccurate information that harmed customers. The false information includes incorrect interest rates, inaccurate payment schedules, and outdated fee data.
- What went wrong: The bot hallucinated or relied on outdated internal documents.
- Why it failed: The chatbots lacked a real-time data feed and a guardrail to prevent incorrect financial details.
- What could have prevented it: The bots needed live data syncing and human confirmation paths.
- Industry lesson: Finance bots must stay tethered to updated and verified financial details.
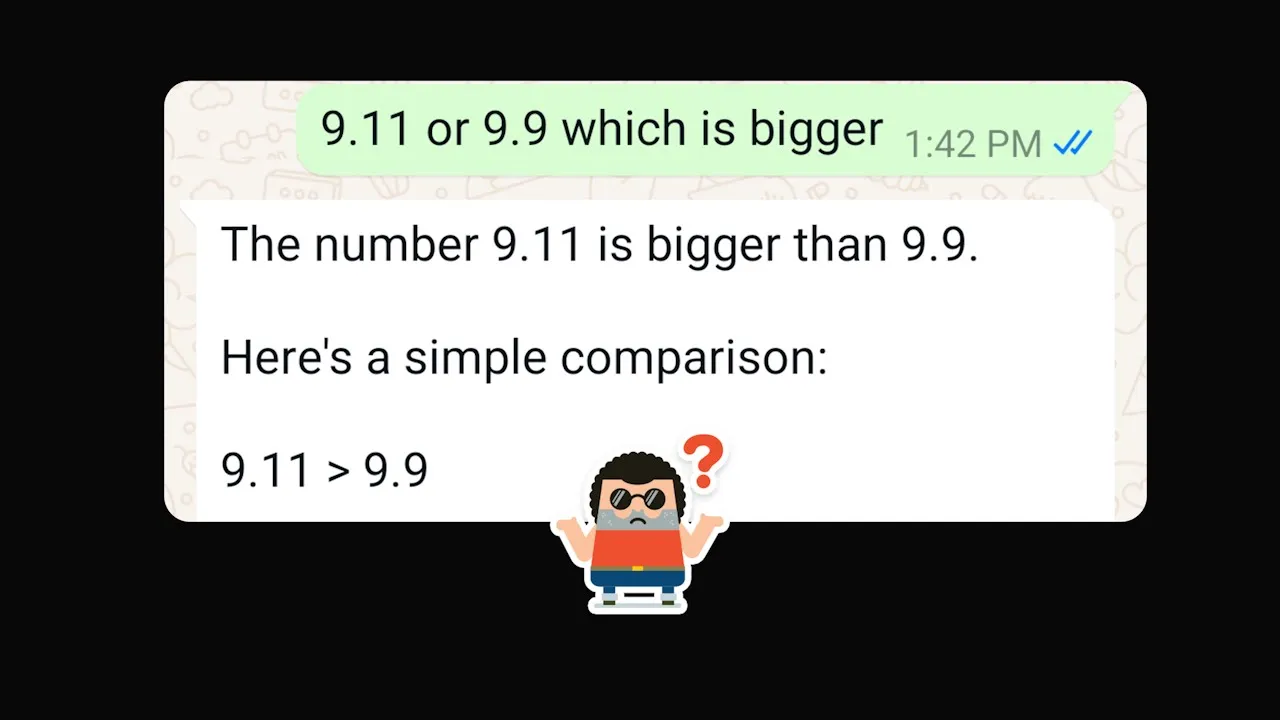
9. AI’s basic math meltdown
Several major chatbots, including ChatGPT and Meta’s AI assistant, produced wildly wrong answers to straightforward math questions. Reporters and researchers documented examples of these chatbot math fails, including the following:
- ChatGPT confidently stated that 953×987=941,961, even though the correct product is 940,611.
- Meta’s AI misjudged simple decimal comparisons, such as incorrectly stating that 9.11 is greater than 9.9.
- What went wrong: Language models guessed the answer based on numeric sequences rather than calculations.
- Why it failed: The chatbot relied on text-prediction patterns instead of actual computation, so it confidently produced incorrect numbers without recognizing the error.
- What could have prevented it: Integrating a verified calculator engine, using a math plugin, or routing calculation requests to a safe fallback would have prevented these errors. Developers could also have flagged math-related prompts for human review.
- Industry lesson: Even small arithmetic mistakes erode trust in the product. Designers learned that bots must either avoid calculations entirely or pair text-based models with tools that guarantee accuracy.
10. Children’s AI toy’s inappropriate answers
A popular AI-enabled toy shocked parents when it answered simple questions from kids with spicy, dangerous, and age-inappropriate content. Videos of the toy circulated across TikTok and parenting forums. This led to many people testing the toy themselves, and the funny responses went viral.
- What went wrong: The toy responded to open-ended questions without age filtering.
- Why it failed: The toy’s bot had no built-in topic limits or oversight from trained reviewers.
- What could have prevented it: The toy would have benefited from guardrails, content filters, and pre-launch testing with actual parents.
- Industry lesson: Kid-facing AI requires strict safety rules that never slip.
5 tips on how to avoid chatbot disasters
You can spot trouble before a launch by following this practical checklist: Define your chatbot’s scope, test every branch thoroughly, add guardrails, update intents often, and track performance. These best practices will reduce chatbot mistakes and protect your company’s reputation.
Tip 1: Define the scope and train with real data
Before you start training a bot, choose the topics you want it to handle, gather the correct information, and train it with sources you trust. This will give your users clear, consistent answers.
Jotform AI Chatbot Builder allows you to upload your docs, FAQs, and internal guidelines to hone the bot’s voice and accuracy.
Tip 2: Test your scripts before launch
Test your bot using different accents, writing styles, stress phrases, and half-finished questions. This will reduce AI fails that could frustrate your customers.
Jotform’s instant response system helps you check speed and clarity while testing.
Tip 3: Add a fallback system
Every bot hits a limit eventually, so your system needs an escape route, such as a button, link, or handoff.
With Jotform, you can add steps for human escalation within the flow, preventing your users from hitting a conversational wall.
Tip 4: Regularly update intents and language models
You update your intents and model training as your company grows. New products appear, and old rules change. You refresh your bot’s knowledge base often. Jotform makes this easier with the AI Chatbot Builder, which lets you retrain the bot with updated files instead of rebuilding everything from scratch.
Tip 5: Track performance through analytics and customer feedback
Analytics help you spot spikes in failure rates, phrases that confuse your bot, and conversations that drag on too long. When you embed the Jotform AI Chatbot anywhere on your site, you can see how users interact with it and how the bot performs.
Building smarter chatbots that don’t fail
These examples of recent chatbot failures demonstrate how bots going off script can undermine your company’s reputation and trustworthiness. Each failure is a lesson in better design, defined limits, clean training data, and strong ethics.
AI bots are constantly improving. Rather than aiming to build the perfect bot, take measures to catch issues quickly. Protect your brand by testing your scripts, watching your metrics, correcting issues, and establishing human fallback options.
Your AI bot should engage your customers, not frustrate them. If you want a simpler way to build your bot, Jotform AI Chatbot Builder can help. With the right tools, your bot will answer questions correctly, guide customers, and avoid the toughest chatbot design challenges.
This article is for UX designers, AI product owners, digital support teams, and anyone who wants to avoid high-profile chatbot failures by understanding where real-world bots go wrong and how to design AI systems that deliver reliable, respectful, and intelligent customer experiences.
FAQs
A chatbot stops working when it loses access to the data or rules it needs or it receives more traffic than expected. Sometimes the bot has old information, and sometimes a user asks a question it has never learned how to answer.
Inundating a chatbot with traffic or purposely asking it questions to lead it off track can cause operative bots to fail.
Failure occurs because teams rush to launch without defined goals, clean data, or fail-safes. Many companies underestimate the importance of ongoing monitoring and correction.








































































Send Comment: